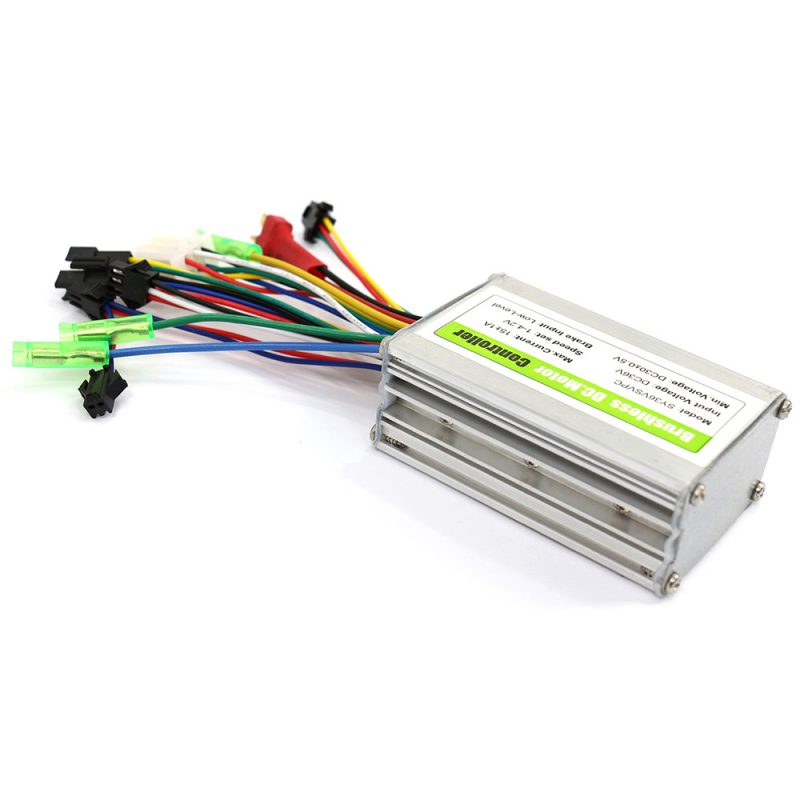
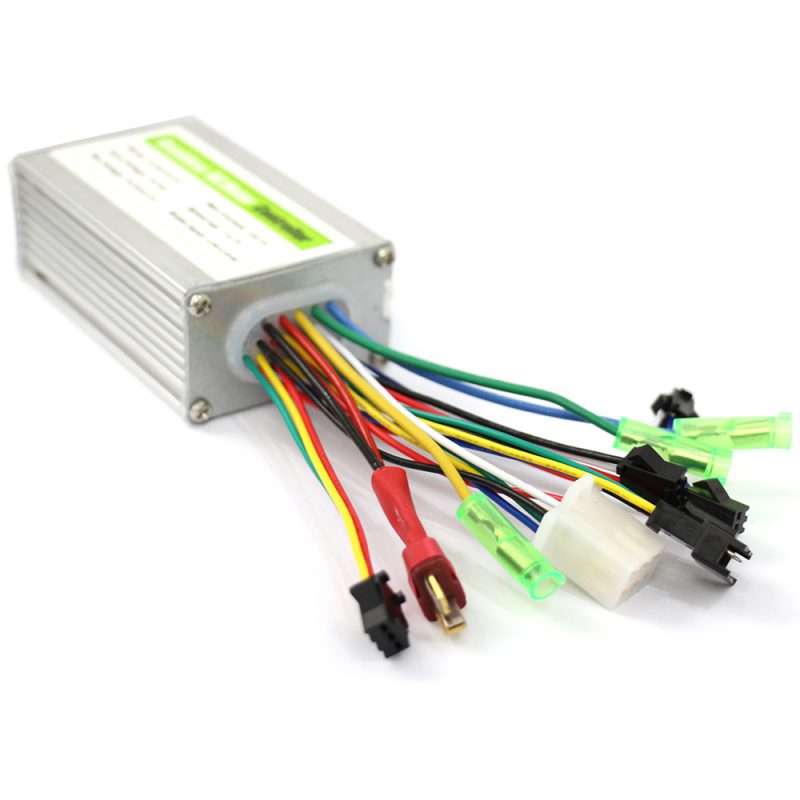
One of the most important features on an electric bike is the controller. It basically acts as the brain of the e-bike and helps you to manage every aspect of the bike. By connecting all the electrical components on the e-bike, including the battery, motor, and throttle; the controller allows you to control the power from the motor, speed of the bicycle, acceleration, etc.
So, if you are an electric bike enthusiast looking to purchase your first battery-powered bicycle, you might want to get familiar with the various aspects of the controller for a great experience. Below is everything you need to know about electric bike controllers.
1.What is an electric bike controller?
The electric bike controller is one of the main parts of an electric bike, it is the brain of the e-bike, controlling the motor’s speed, start, stop. It is connected to all the other electronic parts such as the battery, motor, and the throttle(accelerator), display(speedometer), PAS or other speed sensors if exist.
A controller is composed of main chips ( microcontrollers) and peripheral components ( resistors, sensors, MOSFET, etc ). Generally, there are PWM generator circuit, AD circuit, power circuit, power device driver circuit, signal acquisition and processing circuit, over-current and under-voltage protection circuit inside the controller.
2. How Do E-bike Controllers Work?
The controller gets energy from the bike’s battery and channels it to the motor depending on the sensor and user inputs.
By twisting the throttle, you’ll be able to regulate the power being sent to the e-bike controller, which subsequently controls the bike’s speed.
The controller monitors the speed, acceleration, motor power, battery voltage, pedaling activity, among other functions on the bike. It also controls the amount of pedal-assist you get when riding your bike.
3. What is the Specific Function of the Electric Bike Controller?
The core function of the controller is to take inputs from all the electric components, i.e. speed sensor, throttle, battery, display, motor, etc. and determine what to be signaled in return. It also has other multiple protection functions that may vary between controller designs. These include:
Low-voltage Protection- The controller watches over the battery voltage and shuts down the motor whenever the voltage is too low. This serves to safeguard the battery against over-discharge.
Over-voltage Protection- The controller also monitors the battery voltage so that it does not over-charge. It will shut down when the voltage is too high, ensuring that it is protected.
Over-temperature Protection- The e-bike controller further monitors the temperature of the Field-effective Transistors and shuts down the motor whenever they become too hot. As such, FET power transistors are protected.
Over-cut Protection- The controller also reduces the current flowing to the motor if the current is too much. This protects the motor, as well as the FET power transistors.
Electric Bike Controller on a bike
Brake Protection- The controller shuts down the motor during braking despite other signals being taken by the e-bike controller. For instance, if you apply the brakes and throttle simultaneously, the brake function takes precedence.
4. What are the Different E-bike Controller Types?
Electric bike controllers can be categorized according to a number of criteria. Some of the common types include:
Brushless DC motor controllers
The brushless DC motors are probably the most popular motors controllers. They are brushless and feature permanent magnets. They are also pretty reliable and offer a higher efficiency despite their relatively modest design. Generally, everything on the brushless DC motor controllers is simple, including their operation and service.
This type of controllers has 3 phases that are controlled using a set of keys, as well as at least 2 transistors per phase.
Brushed DC motor controllers
These motors come with permanent magnets to go with a connector. They have a much simpler design with a set of keys that regulate the current being supplied to the engine. These controllers are, more often than not, used on the smaller electric vehicles such as scooters, pedelecs, electric bikes, other light EV, etc.
While there are other types of controllers, these are rarely seen and mostly used by extreme DIY hobbyists and enthusiasts. For an ordinary person looking to get an e-bike, the main choice is either a BLDC or DC.
BLDC controllers for motors with Hall Sensors
These are simple controllers that are based on the Hall effect. These determine the position of the rotor according to the stator. The stator is the fixed part of the motor whereas the rotor is the rotating part.
Hall sensors are also referred to as rotary encoders since they determine the rotor’s position
5. How Do I Choose an E-bike Controller?
When choosing a controller for your electric bike, it is crucial that you find one that is compatible with other bike parts such as the motor, display, battery, etc. The following factors ought to be considered:
Controller driving type-Is it a sine wave or square wave controller?
Both of these come with their own advantages and disadvantages. For instance, sine wave controllers are favored because of their lower noise production and greater efficiency when going uphill or when carrying a heavy load. These controllers also offer you smoother and more predictable control over general operations.
On the downside, sine wave controllers will cost you more and can only function with matched motors. They also consume much more power.
When it comes to square wave controllers, people prefer them as they are more affordable and for their ability to function with different motors. These provide higher efficiency during sudden braking or acceleration, as well as higher utilization of power voltage.
Some of their low points include high noise production and non-smooth or punched control. They are also less motor efficient when scaling hills.
Is it a Hall Sensor drive, non-Hall sensor, or dual-mode controller?
Generally, if the motor features a Hall sensor, the controller is supposed to be Hall-sensor or dual mode. A Hall sensor in the motor senses the motor rotation and the controller outputs the corresponding voltage depending on the sensor signals.
It is more stable and has lower power consumption, as well as bigger start torque. If the motor Hall gets damaged, the controller may prompt an error and seize working while a dual-mode controller continues to work well.
Controller voltage- 24V or 36V or 48V or 60V…?
The voltage of the controller should match that of the battery and motor.
Controller current (rated and max currents)
The controller current is supposed to be smaller than the battery’s output current. Generally, the max current is 25A for a 9-MOSFET controller, 18A for a 6-MOSFET controller, 40A for a 15-MOSFET controller, etc.
6. About the common phenomenon of HOTEBIKE electric bike controller: (Controller damage may lead to the following phenomena, but if this problem occurs, it is not necessarily a damaged controller)
1. The error code 03 or 06 appears on the LCD display. 2;
2. Intermittent work of bicycle motors. 3;
3. LCD black screen. 4;
The LCD can be turned on, but the motor does not work;
For more details, please contact HOTEBIKE.
Translated with www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)
Here is an article mainly describes the HOTEBIKE controller (Click on the link to view)
HOTEBIKE official website:https://www.hotebike.com/
LEAVE US A MESSAGE
 hotebike
hotebike

